Creating an e-learning platform for children with down syndrome
Overview
Children with Down Syndrome are commonly known for the genetic disorder that is due to the existence of an extra copy of chromosome 21. These children suffer from both medical and physical impairment, however, the degree of impairment may vary for each child.
As a design researcher, my goal was to highlight issues and limitations of eductional tools for children with down syndrome and drive out user needs by providing a hypothetical solution.
Activities
Interviews, Market Analysis
Personas, Paper prototyping, Wireframes, Architecture
Prototyping, Preference & Eye Tracking Test
Research
Understanding the system
Medical issues
Students with Down syndrome may: need to go to the school nurse for medications when necessary, miss class time due to frequent doctor visits.
Additional assistance
Children with Down Syndrome need visual and auditory accommodations for classroom instruction, need extra time and assistance with classwork and require therapeutic staff support in the classroom.
Parents' involvement
Many teacher showed concerns for the lack of parents' involvement in the learning process of their child. They stated that if parents were more involved alongside teachers, learning could be much faster.
Conducting a market research
In order to understand the current landscape of eductional tools for the children, we also conducted a market research. While we did an intensive research on various tools like "MathDS", "WAVE", "See and Learn", we learnt several things which formed our HMW statement.
- 1. Each tool is known for targetting one or two problem areas.
- 2. Most resources online doesn't teach parents a way to evaluate their child's progress.
- 3. These tools are harder to find online.
Design opportunity (HMW)
How can we build an easy-to-use platform to help make educational tools for children with down syndrome more accessible?

Ideation & creation
User persona
To understand our users better, we divided them into two groups to focus on their individual needs. Below I've highlighted the major characteristics of both of our user groups.
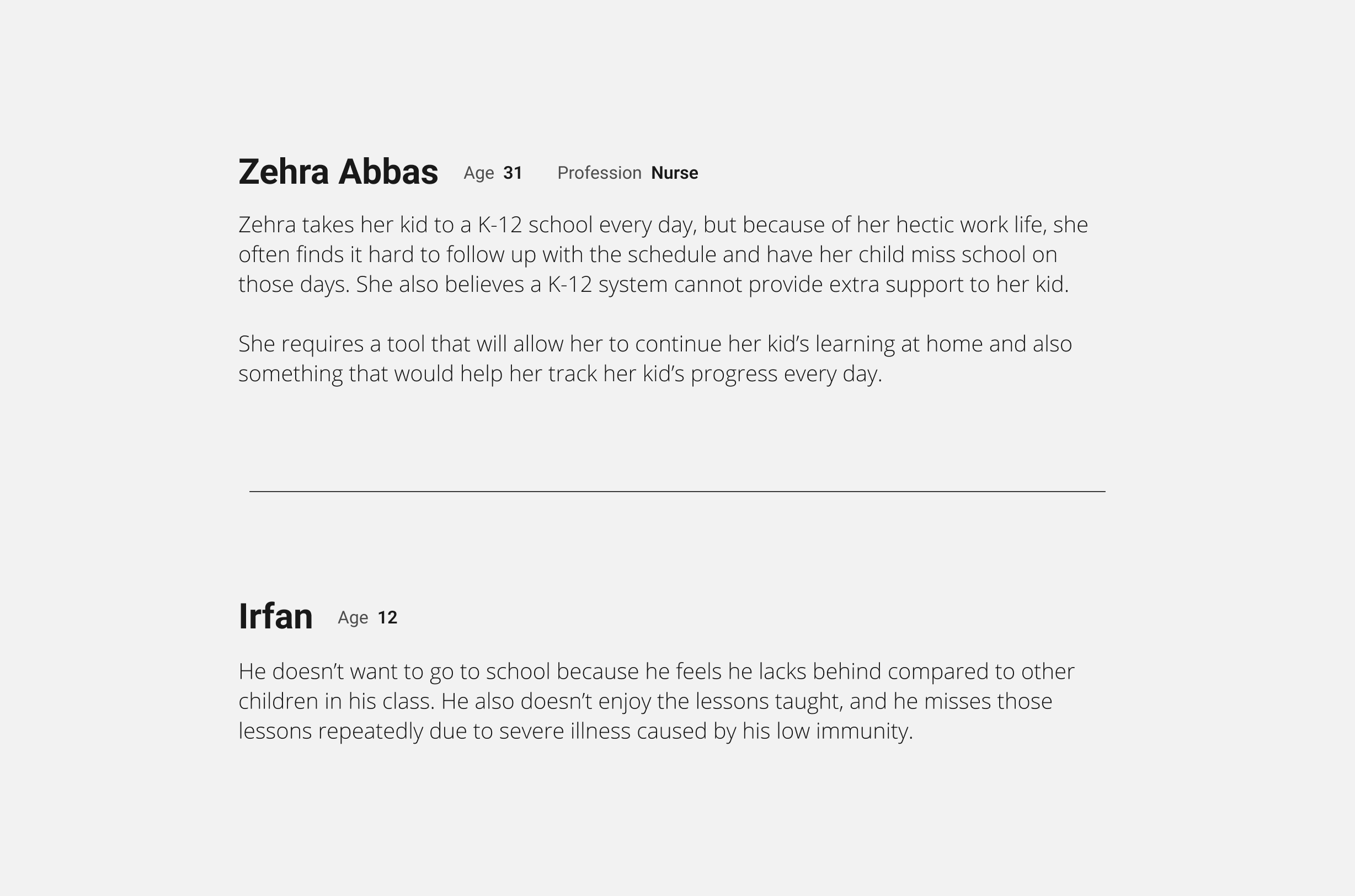
The initial personas were hypothetical and were required to create the user's mental model.
Paper prototyping
We used paper prototypes as a quick way to validate our understanding of user needs show experimenting with the key stakeholders of the project. This activity gave us a starting direction for initial designs.
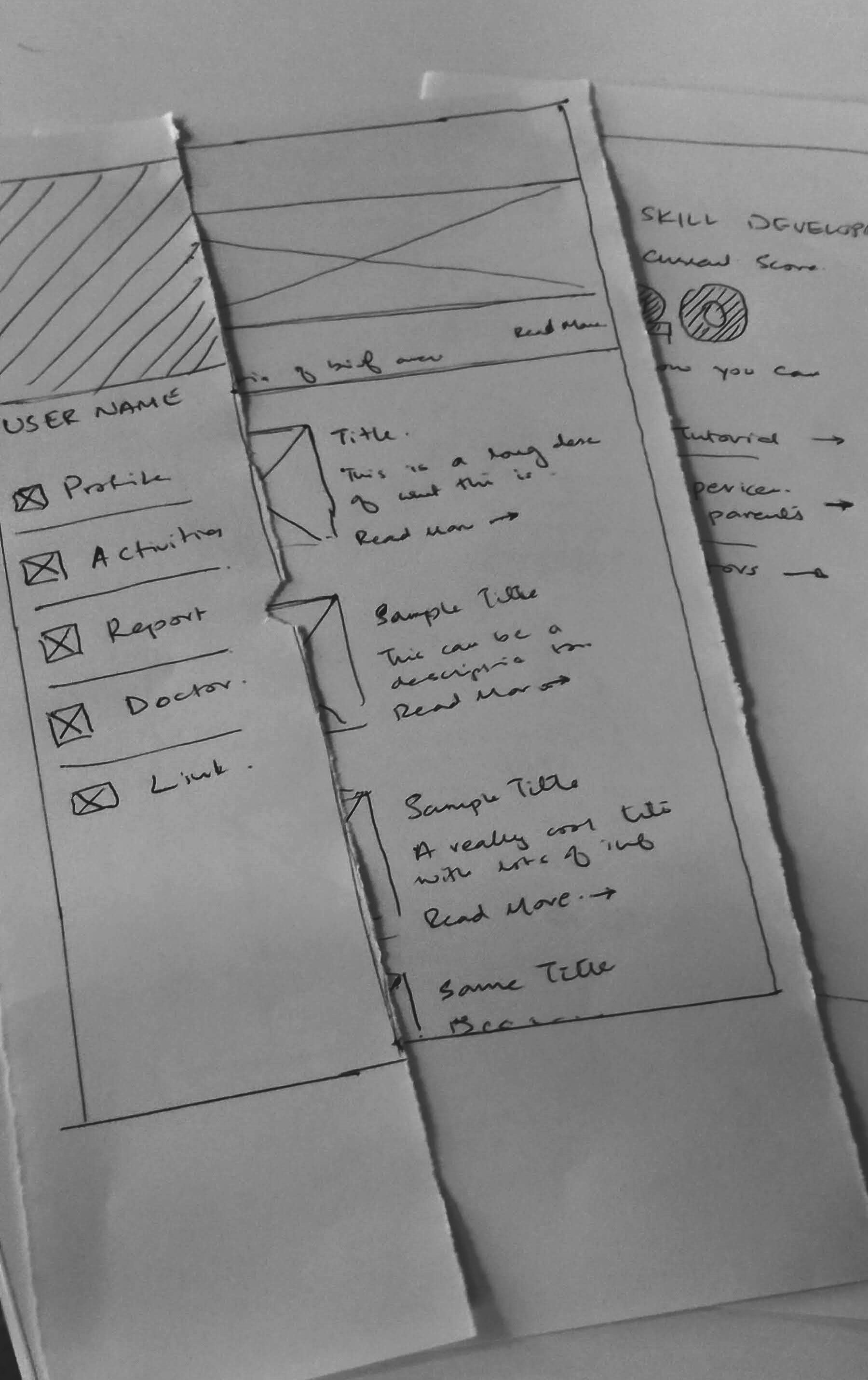
Above image shows a paper prototype of the side menu.
Initial designs
After gathering requirements, we drafted an initial design focusing on two main things, i.e. user flow and content layout.
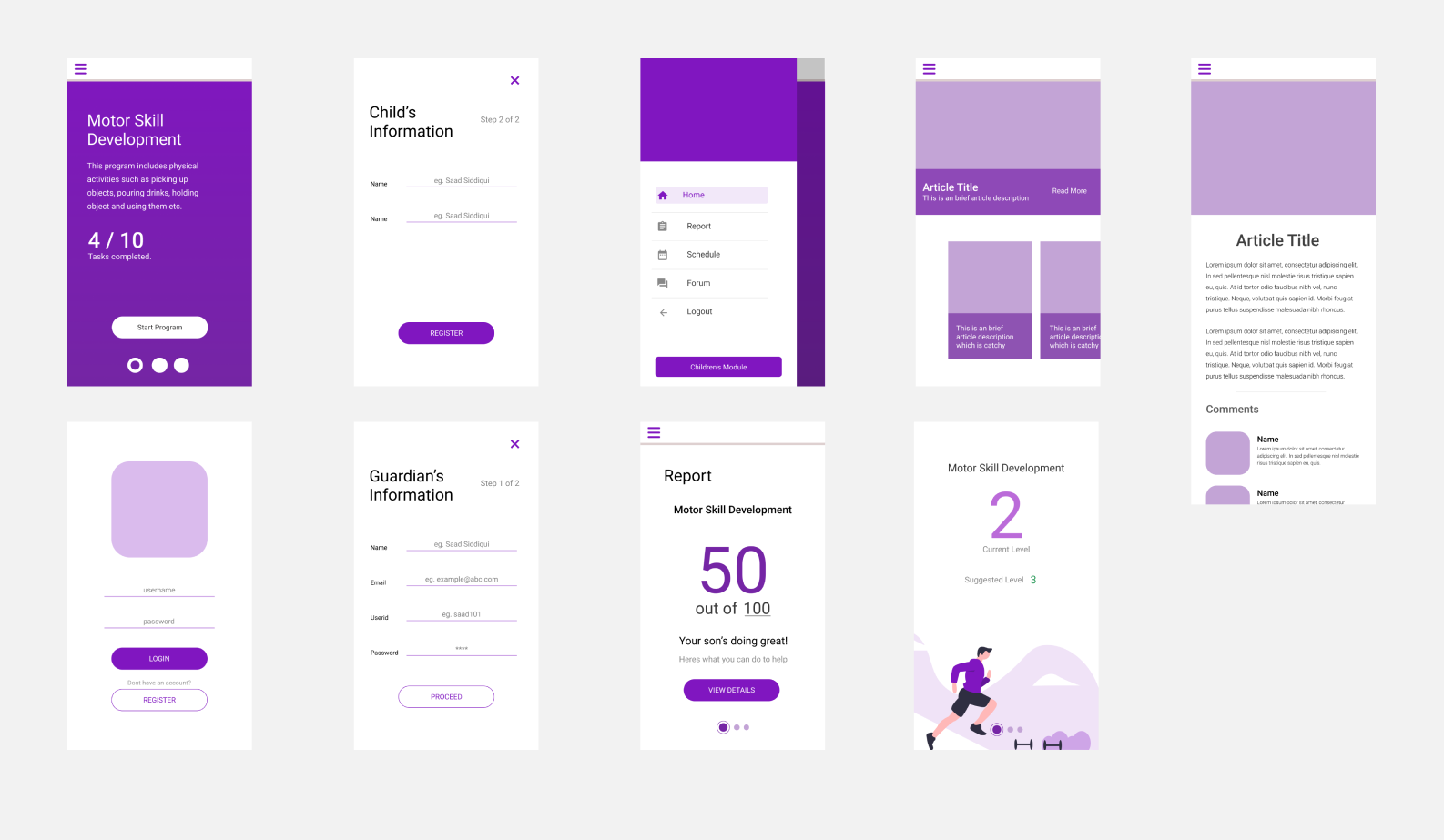
Evaluation & testing
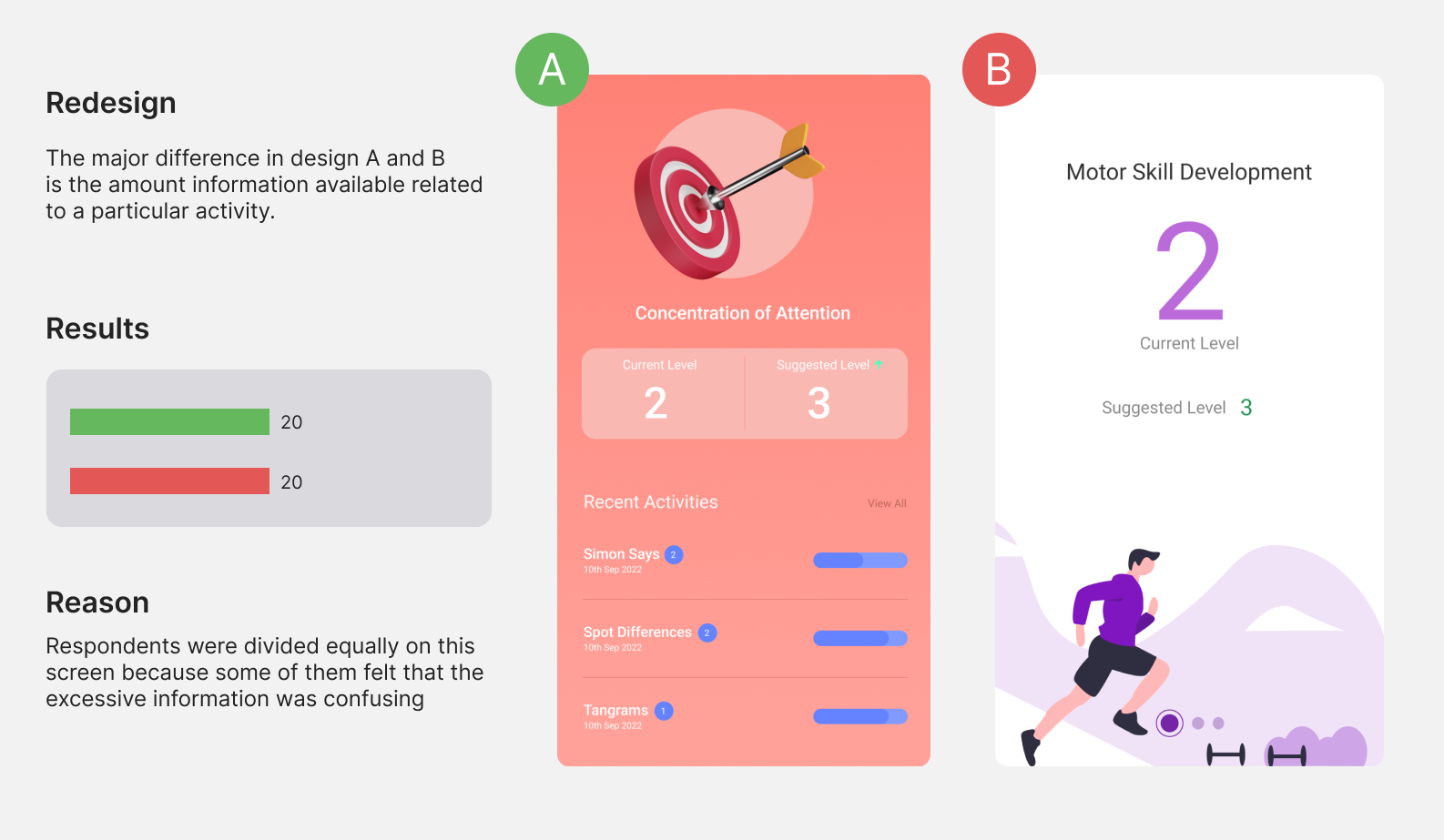
Preference testing
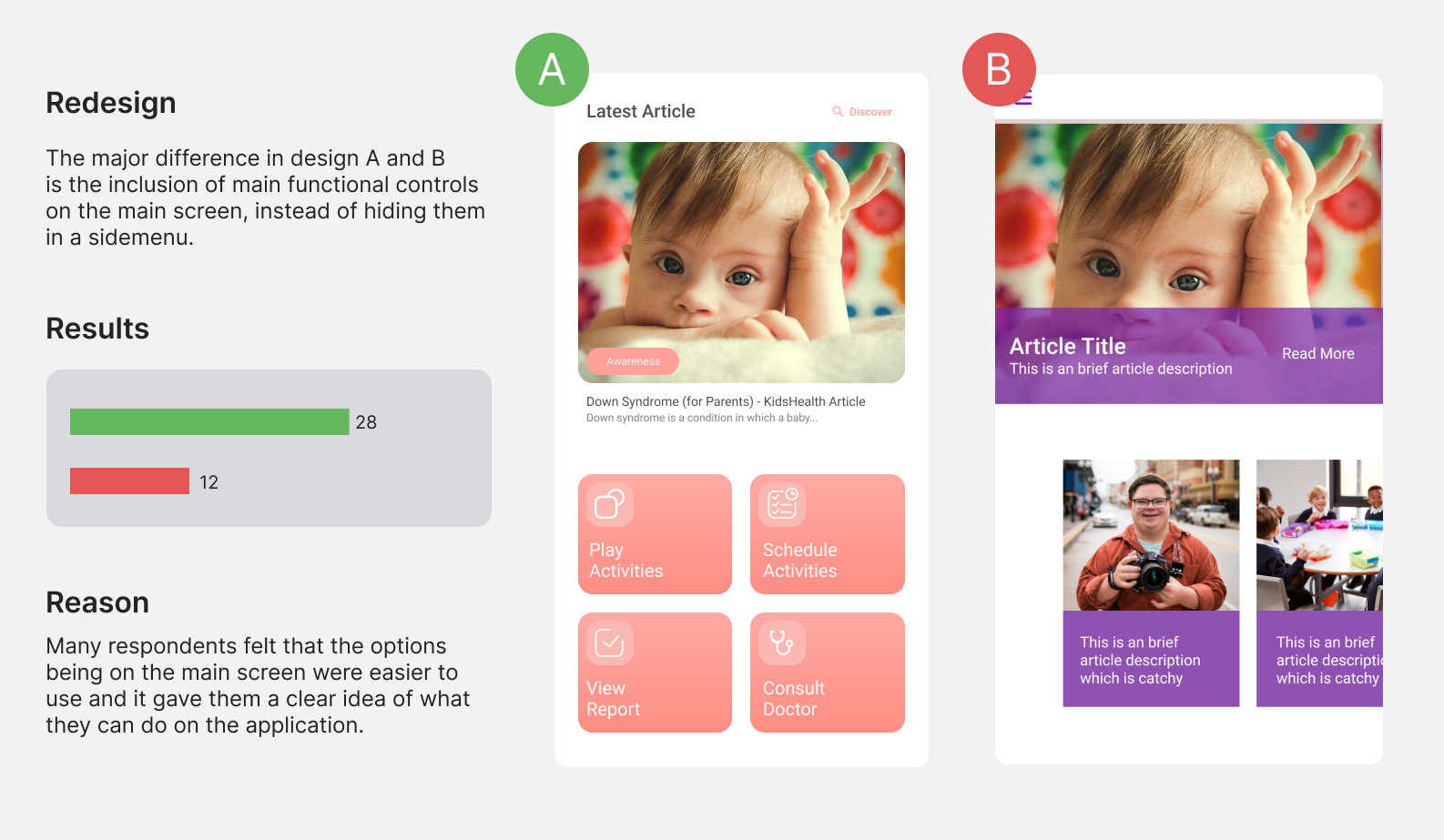
For evaluating our solution and gain feedback, we conducted a preference test with 40 people recruited carefully using our initial personality definition. Test results of two screens are shown below.
Eye-tracking test
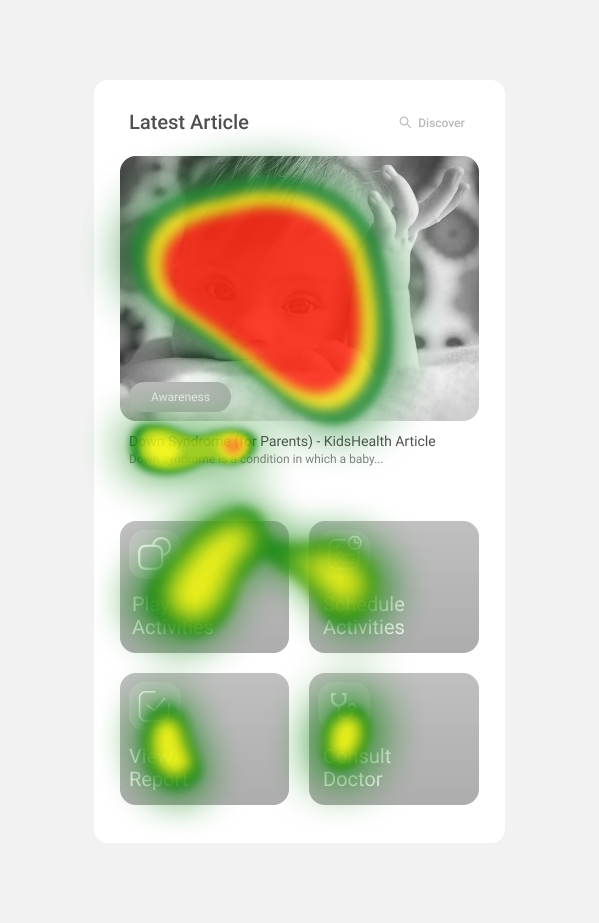
Since our initial test gave us an insight about the user's preference for a certain amount of information on the screen, we conducted a few eye tracking tests on main functional screens. One of those results is given below.
Key points
1. More than 70% (avg) prefered new designs due to easier access to
actionable items.
2. It was observed that people preference for quantity of data on a screen
had a direct relation with their digital literacy.
3. Eye tracking results directed our design decisions to organize information and actions in much better
way.
Conclusion
According to the research question at the beginning of this study, we have found that currently there is a gap in the discoverability of educational tools for children with Down Syndrome and the unavailability of one coherent application to assist parents in taking part in their child's educational needs.